Best 5 Camera Robots
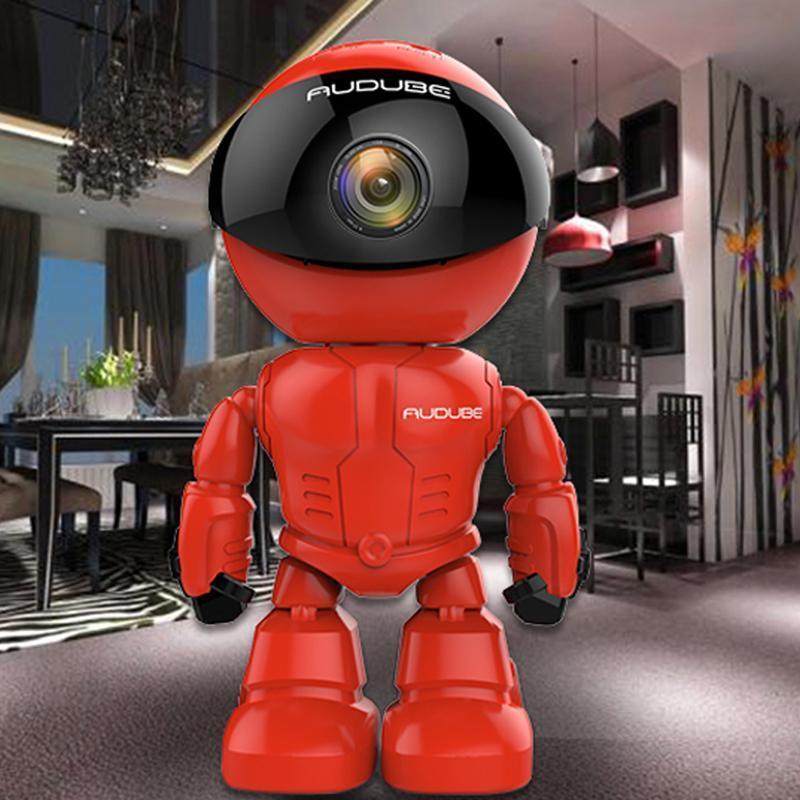
Best 5 Camera Robots 1. Reolink Trackmix PoE 4K Security Outdoor Camera Dual-Lens Motion Tracking PTZ camera 6X Zoom Animal Car Human Detect CCTV IP Cam [caption id="attachment_2578" align="aligncenter" width="1000"] Reolink Trackmix PoE 4K Security Outdoor Camera Dual-Lens Motion Tracking…
Read More









 by
by